INSPIRASI: Charging Optimization for Electric Vehicle Fleets
Research Motivation
The rapid transition toward sustainable urban transportation has accelerated the deployment of Electric Vehicles (EVs) in smart cities, offering a promising solution to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. However, this large-scale adoption introduces new complexities for both energy and transportation infrastructures. Numerous studies have explored EV integration into the grid, addressing charging station placement, battery degradation, and power load balancing. Recent literature emphasizes the need for smart, data-driven charging strategies that align with grid capacity, battery degradation, and user demand. Additionally, route optimization for EVs is gaining importance, as it directly impacts vehicle energy efficiency and user experience. Research also shows that external factors such as weather, terrain, and driving behavior significantly influence EV energy consumption and must be considered in optimization models. Despite these advances, current approaches often treat routing and charging independently or rely solely on either optimization or machine learning techniques, leading to suboptimal performance in real-world settings.
The motivation for this research stems from the increasing adoption of EVs in logistics and transportation, and the pressing need for charging strategies that are cost-effective, battery health-aware, and grid-compliant. Through this initial exploration, we identified several key challenges that will guide our subsequent phases. These include handling grid limitations and demand response signals, addressing battery degradation from Vehicle to Grid (V2G) cycles and frequent fast-charging, coping with fluctuating electricity prices, and operating under limited infrastructure with constraints on charging ports and station capacities. Moreover, integrating V2G capabilities while ensuring the fulfillment of rental or operational demands presents a complex optimization problem.
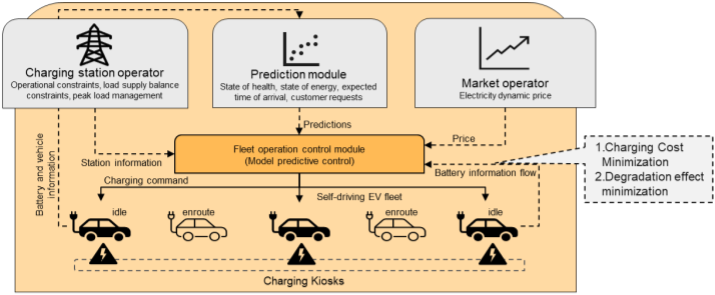
Problem Statement
This project addresses the gap by proposing an integrated framework that combines machine learning and mathematical optimization to tackle EV fleet charging and routing challenges holistically. The key problem is to develop intelligent algorithms that can schedule charging while considering grid constraints, battery health, V2G, service level constraints, and dynamic electricity pricing. Simultaneously, the framework must support route planning by focusing on understanding how variables such as EV model and range, weather conditions, terrain type, traffic conditions, vehicle load, battery load, and driving style impact energy consumption and, consequently, route feasibility. A significant limitation in existing models is the lack of real-time adaptability and personalized decision-making for diverse EV fleets. This research aims to overcome these limitations by developing hybrid, multi-factor models capable of capturing the operational intricacies of EVs in smart city (digital twin) environments.
Research Objectives
This research addresses critical challenges of EV fleet charging and routing optimization. The primary research objectives proposed are as follows:
- Development of smart hybrid algorithms (combining mathematical optimization and machine learning) to optimize the charging strategy for EVs while considering dynamics of the EV batteries and infrastructural limitations posed by the energy networks.
- Development of pricing methodologies for demand responsive charging behavior of EV fleet.
- Development of multi-factor models to capture the impact of weather conditions, terrain type, traffic conditions, vehicle load, battery load, and driving style on EV energy consumption and range. This will enable efficient route planning for EVs including intermediate charge planning.